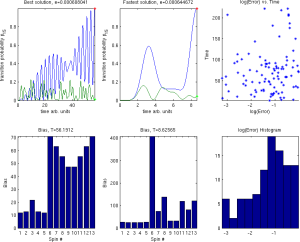
F. C. Langbein, S. G. Schirmer, E. Jonckheere. Time optimal information transfer in spintronics networks. Proc. IEEE 54th Annual Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), pp. 6454-6459, Osaka, Japan, December 15-18, 2015. [DOI:10.1109/CDC.2015.7403236] [arXiv:1508.00928] [PDF]
Propagation of information encoded in spin degrees of freedom through networks of coupled spins enables important applications in spintronics and quantum information processing. We study control of information propagation in rings of $\tfrac{1}{2}$-spins with uniform nearest neighbour couplings forming a ring with a single excitation in the network as simple prototype of a router for spin-based information. Specifically optimising spatially distributed potentials, which remain constant during information transfer, simplifies the implementation of the routing scheme. However, the limited degrees of freedom makes finding a control that maximises the transfer probability in a short time difficult. The structure of the eigenvalues and eigenvectors must fulfill a specific condition to be able to maximise the transfer fidelity. While there are many potential structures that fulfill this condition, we choose a specific one, which in turn significantly improves the solutions found by optimal control.
![]() This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.